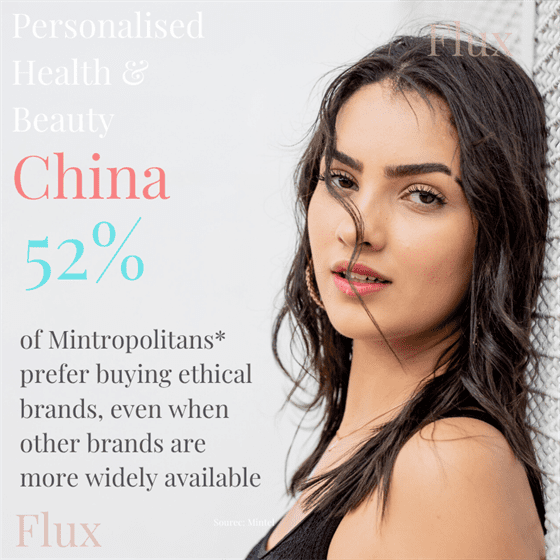
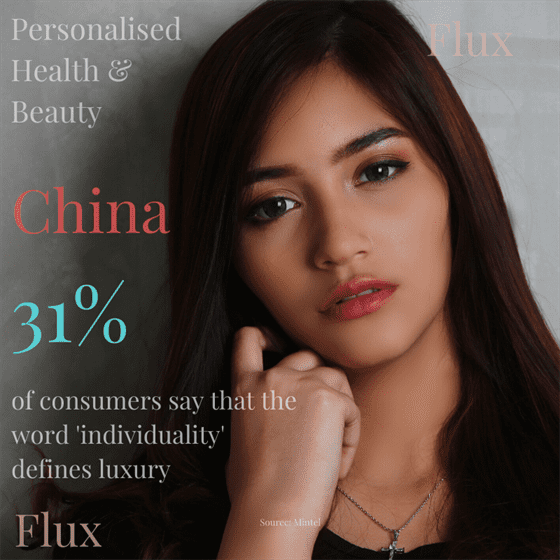
Humans the Microbial Super Organism
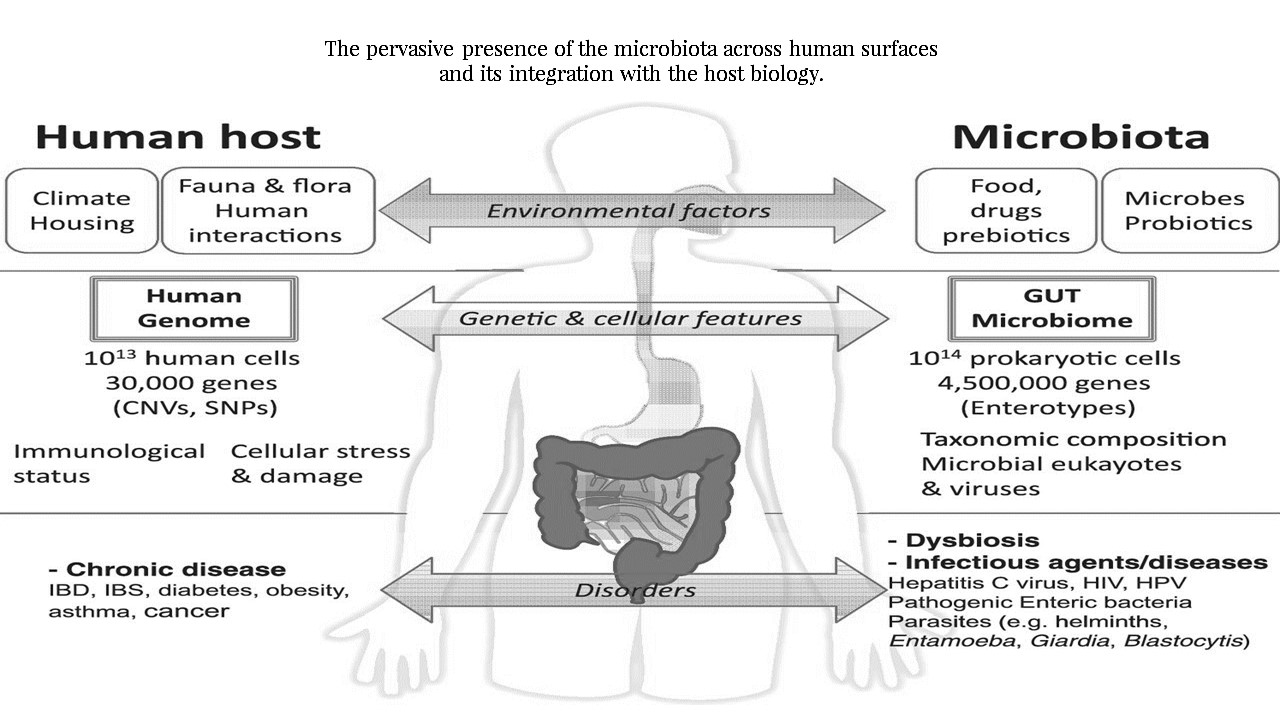
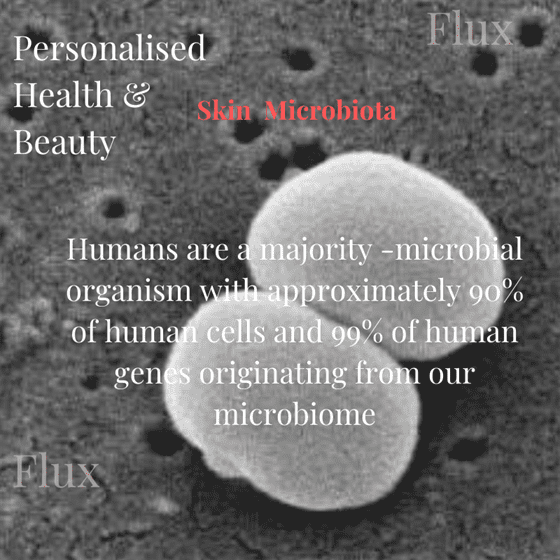
The body is an ecosystem of interconnected human and non-human parts. Humans are a majority -microbial organism with approximately 90% of human cells and 99% of human genes originating from our microbiome rather than from the mammalian part of our body.
Microbiomes Your Personal Fingerprint.
According to Cornell University, human microbes exert control over the development and function of our physiological systems.
This includes but is not limited to our immune, gastrointestinal and neurological systems. To the extent of significantly altering human behaviour and health.
The holy grail, in precision medicine is the ability to match a cure to a disease such as cancer or diabetes based on the genetic code of a patient.
Hence, the advancement in personalised health depends upon our capacity to analyse the human microbial and mammalian genetic code. In other words, in order to effectively treat human disease. It may be prudent, to view patients as a multi-species superorganism.
Every individual is inhabited and surrounded by his or her own signature microbial cloud. These microorganisms are responsible for human health and well-being.
A low diversity of microorganisms is associated with a plethora of diseases including allergy, diabetes, obesity, arthritis, inflammatory diseases and even neuropsychiatric disorders.
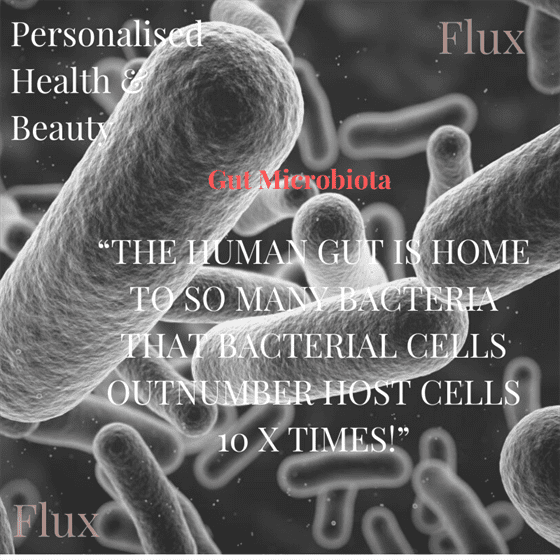
““The human gut is home to so many bacteria that bacterial cells outnumber host cells 10 X times!””
For humans to be and remain healthy, exposure to microorganisms at birth and the interaction with the appropriate microbiome assembly during childhood is critical for the inducement and establishment of an adaptive immune system.
Microorganisms are prerequisite for the initiation of memory B and T cells that are essential to combat various pathogens. Also, the correct microbial-based education of immune cells may play a critical role in preventing autoimmune diseases and cancer.
Individuals with a diverse, microorganism, can regulate and maintain a healthy human system. The human body is estimated to be composed of 3 x10 to the power 13 eukaryotic cells and 3.9 x 10 to the power 13 of colonising microorganisms.
Resulting in near equal parity between the host cells and microbiota within an individual. The largest concentration of microbes is found within the gut, skin and oral cavity.
Published by Oxford University Briefings in Bioinformatics, Vol 13, Issue 6, Nov 2012
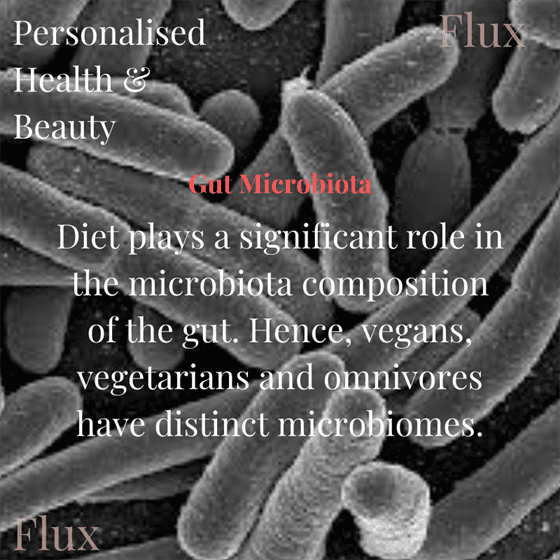
Diet plays a significant role in the microbiota composition of the gut. Hence, vegans, vegetarians and omnivores have distinct microbiomes.
It is obvious that the determinants of human health are not solely controlled by an individual’s genomes. It seems that many disease pathologies are involved in the interplay between the human body.
The external environment and the complexity of the microorganism residing in the mucosal surfaces of our respiratory tract, urogenital tract, gastrointestinal tract, and skin.
Applications of Microbiomes – Skincare
The skincare market is estimated to be worth US$100bn according to Euromonitor. MarketandMarkets.com, stated that the human microbiome market is expected to be worth US$658m by 2023.
In 2016 venture capitalists invested US$600m up 1000%. More than the sum invested between 2011-2015.
In response to the ongoing shift towards more personalised health and beauty. And the increasing awareness by the general public of the benefits of a healthy microbiome.
Skincare brands in Europe and the USA have launched prestige bacteria infused skin care products, developed to work with skin microbiota.
UK skincare brands launched more bacteria infused skin care products than their international rivals. According to Mintel, with 37% of the worlds launches coming from the UK, followed by 25% in the USA and 15% in France.
Also, skincare practitioners are deploying advanced technologies to;
Understand the impact of microbiomes on skin
Explore the link between microbiota and healthy skin
Mitigate dermatological problems, through the deployment of probiotics and prebiotics to restore the balance to skin flora
Skincare manufacturers are engaged in the development of new active ingredients. Leveraging, macrobiotics to develop skincare therapeutics that activate, protect and balance skin microbiota.
Images of Gut & Skin Microbiota
Analysis conducted by the Human Microbiome Project revealed that, conventional skin care products are responsible for 90% of the chemicals on the skin. That are implicated in the increasing number of skin problems in Western countries.
Common moisturisers, soaps and shampoos can undermine the skin microbiome, due to the antimicrobial preservatives they contain or their alkaline ph.
Hence, several established and new market entrants recognise the market opportunity of skincare products infused with bacteria that collaborate with the skins’ microbiota.
Skincare Manufactures Incumbent in this Space
Companies incumbent in this space included Hcode, a Chinese human microbiome testing company that conducts tests to decode each individual’s microbiome. Loreal’s Lipikare Baume, integrates the bacterium Vitreoscilla filiformis to support microbial diversity.
Avene’s XeraCalm range, claims to stimulate the production of antimicrobial peptides. Melatogenine AOX Probiotics [KA1] by Gatineau Paris. In the UK British company REN, launch the Citrus Limonum Prebiotic Hand Cream, the product contains alpha-glucan oligosaccharide, a prebiotic that prevents disease caused by pathogenic bacteria. The Belgian company, Gova Ingredients, sells Biolin, which is a prebiotic based on gluco-oligosaccharide.
AOBiome is an American start-up leading in the skin microbiome market and is a pioneer in the development of products that modulate the skin microbiome by chemical reactions. The company recently launched the Mother Dirt range.
So, What Is Skin Microbiota?
Human skin functions as the exterior interface of the human body with the environment. Skin operates as a physical barrier to invading foreign pathogens, whilst providing a home to commensal microbiota.
In the ‘human skin microbiome’ published by Nature Reviews Microbiology. The desiccated nutrient-poor, acidic environment of the skin contributes to the adversity that pathogens face with colonising skin. However, human skin is still colonised by a diverse array of microbiota.
The microorganisms that inhabit the skin, a collection of bacteria, fungi and viruses vary between individuals, and between different sites on the skin.
An understanding of the factors that drive the unique variability of the microorganisms, and the functional significance of resident microbes on the skin, is only partly understood. However, there is evidence that the host genetic and environmental influences play a major role.
Normal physiological conditions must maintain homeostasis between the microbiome and the host. Homeostasis refers to ensuring that the equilibrium of the internal system, is maintained. This could be the pH levels of different sections of the skin.
Experiments conducted by scientist to describe the skin and test the biological function of surface microbiomes. Has provided new insights into the links between human physiology and skin microbiota.
The Consumer Perspective
As consumers become sophisticated in expanding their knowledge on the impact of man- made materials on the environment. There is this ongoing movement to incorporate natural ingredients in their everyday lives.
One industry impacted by the desire of consumer engage in activities that are complimentary to their wellbeing and the health of the planet is the skincare industry.